Summary
Chapter 6 of Capital by Karl Marx explores the pivotal concept of labor-power as a commodity—a foundational idea in understanding how capitalism functions. Marx argues that the transformation of money into capital cannot occur through mere exchange of goods, but rather through the purchase and consumption of labor-power—the worker’s physical and mental capacity to produce value.
In this chapter, Marx outlines two essential conditions for labor-power to be sold as a commodity:
- The worker must be legally free to sell their labor.
- The worker must be economically forced to do so, having no other means of livelihood or production.
Marx describes labor-power as unique because its consumption creates value, specifically surplus-value—the key to profit in capitalism. The capitalist buys labor-power at its value (determined by the cost of subsistence) but extracts more value than paid through the production process.
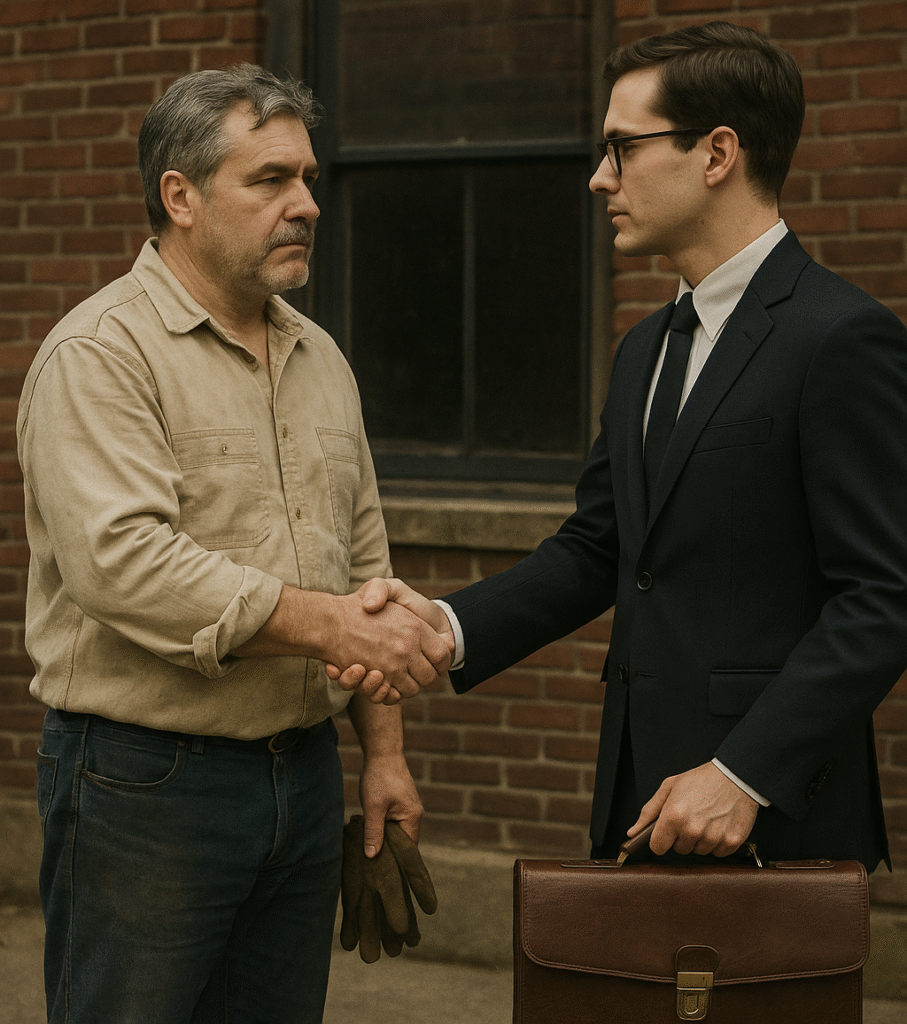
This exchange appears on the surface as one of freedom, equality, and mutual benefit, but Marx reveals it as the beginning of exploitation. The worker, seemingly free, is actually coerced by economic necessity. The chapter closes with the metaphor of entering the factory—the hidden sphere where profit is truly created, signaling the capitalist mode of production.
Chapter 6 – The buying and selling of labor-power
The change of value that occurs in the case of money intended to be converted into capital, cannot take place in the money itself, since in its function of means of purchase and of payment, it does no more than realize the price of the commodity it buys or pays for; and, as hard cash, it is value petrified, never varying.1 Just as little can it originate in the second act of circulation, the re-sale of the commodity, which does no more than transform the article from its bodily form back again into its money-form. The change must, therefore, take place in the commodity bought by the first act, M—C, but not in its value, for equivalents are exchanged, and the commodity is paid for at its full value. We are, therefore, forced to the conclusion that the change originates in the use-value, as such, of the commodity, i.e., in its consumption. In order to be able to extract value from the consumption of a commodity, our friend, Moneybags, must be so lucky as to find, within the sphere of circulation, in the market, a commodity, whose use-value possesses the peculiar property of being a source of value, whose actual consumption, therefore, is itself an embodiment of labor, and, consequently, a creation of value. The possessor of money does find on the market such a special commodity in capacity for labor or labor-power.
By labor-power or capacity for labor is to be understood the aggregate of those mental and physical capabilities existing in a human being, which he exercises whenever he produces a use-value of any description.
But in order that our owner of money may be able to find labor-power offered for sale as a commodity, various conditions must first be fulfilled. The exchange of commodities of itself implies no other relations of dependence than those which result from its own nature. On this assumption, labor-power can appear upon the market as a commodity, only if, and so far, as, its possessor, the individual whose labor-power it is, offers it for sale, or sells it, as a commodity. In order that he may be able to do this, he must have it at his disposal, must be the untrammeled owner of his capacity for labor, i.e., of his person.2 He and the owner of money meet in the market, and deal with each other as on the basis of equal rights, with this difference alone, that one is buyer, the other seller; both, therefore, equal in the eyes of the law. The continuance of this relation demands that the owner of the labor-power should sell it only for a definite period, for if he were to sell it rump and stump, once for all, he would be selling himself, converting himself from a free man into a slave, from an owner of a commodity into a commodity. He must constantly look upon his labor-power as his own property, his own commodity, and this he can only do by placing it at the disposal of the buyer temporarily, for a definite period of time. By this means alone can he avoid renouncing his rights of ownership over it.3
The second essential condition to the owner of money finding labor-power in the market as a commodity is this – that the laborer instead of being in the position to sell commodities in which his labor is incorporated, must be obliged to offer for sale as a commodity that very labor-power, which exists only in his living self.
In order that a man may be able to sell commodities other than labor-power, he must of course have the means of production, as raw material, implements, &c. No boots can be made without leather. He requires also the means of subsistence. Nobody – not even “a musician of the future” – can live upon future products, or upon use-values in an unfinished state; and ever since the first moment of his appearance on the world’s stage, man always has been, and must still be a consumer, both before and while he is producing. In a society where all products assume the form of commodities, these commodities must be sold after they have been produced, it is only after their sale that they can serve in satisfying the requirements of their producer. The time necessary for their sale is superadded to that necessary for their production.
For the conversion of his money into capital, therefore, the owner of money must meet in the market with the free laborer, free in the double sense, that as a free man he can dispose of his labor-power as his own commodity, and that on the other hand he has no other commodity for sale, is short of everything necessary for the realization of his labor-power.
The question why this free laborer confronts him in the market, has no interest for the owner of money, who regards the labor-market as a branch of the general market for commodities. And for the present it interests us just as little. We cling to the fact theoretically, as he does practically. One thing, however, is clear – Nature does not produce on the one side owners of money or commodities, and on the other men possessing nothing but their own labor-power. This relation has no natural basis, neither is its social basis one that is common to all historical periods. It is clearly the result of a past historical development, the product of many economic revolutions, of the extinction of a whole series of older forms of social production.
So, too, the economic categories, already discussed by us, bear the stamp of history. Definite historical conditions are necessary that a product may become a commodity. It must not be produced as the immediate means of subsistence of the producer himself. Had we gone further, and inquired under what circumstances all, or even the majority of products take the form of commodities, we should have found that this can only happen with production of a very specific kind, capitalist production. Such an inquiry, however, would have been foreign to the analysis of commodities. Production and circulation of commodities can take place, although the great mass of the objects produced are intended for the immediate requirements of their producers, are not turned into commodities, and consequently social production is not yet by a long way dominated in its length and breadth by exchange-value. The appearance of products as commodities pre-supposes such a development of the social division of labor, that the separation of use-value from exchange-value, a separation which first begins with barter, must already have been completed. But such a degree of development is common to many forms of society, which in other respects present the most varying historical features. On the other hand, if we consider money, its existence implies a definite stage in the exchange of commodities. The particular functions of money which it performs, either as the mere equivalent of commodities, or as means of circulation, or means of payment, as hoard or as universal money, point, according to the extent and relative preponderance of the one function or the other, to very different stages in the process of social production. Yet we know by experience that a circulation of commodities relatively primitive, suffices for the production of all these forms. Otherwise with capital. The historical conditions of its existence are by no means given with the mere circulation of money and commodities. It can spring into life, only when the owner of the means of production and subsistence meets in the market with the free laborer selling his labor-power. And this one historical condition comprises a world’s history. Capital, therefore, announces from its first appearance a new epoch in the process of social production.4
We must now examine more closely this peculiar commodity, labor-power. Like all others it has a value.5 How is that value determined?
The value of labor-power is determined, as in the case of every other commodity, by the labor-time necessary for the production, and consequently also the reproduction, of this special article. So far as it has value, it represents no more than a definite quantity of the average labor of society incorporated in it. Labor-power exists only as a capacity, or power of the living individual. Its production consequently pre-supposes his existence. Given the individual, the production of labor-power consists in his reproduction of himself or his maintenance. For his maintenance he requires a given quantity of the means of subsistence. Therefore, the labor-time requisite for the production of labor-power reduces itself to that necessary for the production of those means of subsistence; in other words, the value of labor-power is the value of the means of subsistence necessary for the maintenance of the laborer. Labor-power, however, becomes a reality only by its exercise; it sets itself in action only by working. But thereby a definite quantity of human muscle, nerve, brain, &c., is wasted, and these require to be restored. This increased expenditure demands a larger income.6 If the owner of labor-power works to-day, to-morrow he must again be able to repeat the same process in the same conditions as regards health and strength. His means of subsistence must therefore be sufficient to maintain him in his normal state as a laboring individual. His natural wants, such as food, clothing, fuel, and housing, vary according to the climatic and other physical conditions of his country. On the other hand, the number and extent of his so-called necessary wants, as also the modes of satisfying them, are themselves the product of historical development, and depend therefore to a great extent on the degree of civilization of a country, more particularly on the conditions under which, and consequently on the habits and degree of comfort in which, the class of free laborers has been formed.7 In contradistinction therefore to the case of other commodities, there enters into the determination of the value of labor-power a historical and moral element. Nevertheless, in a given country, at a given period, the average quantity of the means of subsistence necessary for the laborer is practically known.
The owner of labor-power is mortal. If then his appearance in the market is to be continuous, and the continuous conversion of money into capital assumes this, the seller of labor-power must perpetuate himself, “in the way that every living individual perpetuates himself, by procreation.”8 The labor-power withdrawn from the market by wear and tear and death, must be continually replaced by, at the very least, an equal amount of fresh labor-power. Hence the sum of the means of subsistence necessary for the production of labor-power must include the means necessary for the laborer’s substitutes, i.e., his children, in order that this race of peculiar commodity-owners may perpetuate its appearance in the market.9
In order to modify the human organism, so that it may acquire skill and handiness in a given branch of industry, and become labor-power of a special kind, a special education or training is requisite, and this, on its part, costs an equivalent in commodities of a greater or less amount. This amount varies according to the more or less complicated character of the labor-power. The expenses of this education (excessively small in the case of ordinary labor-power), enter pro tanto into the total value spent in its production.
The value of labor-power resolves itself into the value of a definite quantity of the means of subsistence. It therefore varies with the value of these means or with the quantity of labor requisite for their production.
Some of the means of subsistence, such as food and fuel, are consumed daily, and a fresh supply must be provided daily. Others such as clothes and furniture last for longer periods and require to be replaced only at longer intervals. One article must be bought or paid for daily, another weekly, another quarterly, and so on. But in whatever way the sum total of these outlays may be spread over the year, they must be covered by the average income, taking one day with another. If the total of the commodities required daily for the production of labor-power = A, and those required weekly = B, and those required quarterly = C, and so on, the daily average of these commodities = (365A + 52B + 4C + &c) / 365. Suppose that in this mass of commodities requisite for the average day there are embodied 6 hours of social labor, then there is incorporated daily in labor-power half a day’s average social labor, in other words, half a day’s labor is requisite for the daily production of labor-power. This quantity of labor forms the value of a day’s labor-power or the value of the labor-power daily reproduced. If half a day’s average social labor is incorporated in three shillings, then three shillings is the price corresponding to the value of a day’s labor-power. If its owner therefore offers it for sale at three shillings a day, its selling price is equal to its value, and according to our supposition, our friend Moneybags, who is intent upon converting his three shillings into capital, pays this value.
The minimum limit of the value of labour-power is determined by the value of the commodities, without the daily supply of which the labourer cannot renew his vital energy, consequently by the value of those means of subsistence that are physically indispensable. If the price of labor-power fall to this minimum, it falls below its value, since under such circumstances it can be maintained and developed only in a crippled state. But the value of every commodity is determined by the labor-time requisite to turn it out so as to be of normal quality.
It is a very cheap sort of sentimentality which declares this method of determining the value of labor-power, a method prescribed by the very nature of the case, to be a brutal method, and which wails with Rossi that, “To comprehend capacity for labor (puissance de travail) at the same time that we make abstraction from the means of subsistence of the laborers during the process of production, is to comprehend a phantom (être de raison). When we speak of labor, or capacity for labor, we speak at the same time of the laborer and his means of subsistence, of laborer and wages.”10 When we speak of capacity for labor, we do not speak of labor, any more than when we speak of capacity for digestion, we speak of digestion. The latter process requires something more than a good stomach. When we speak of capacity for labor, we do not abstract from the necessary means of subsistence. On the contrary, their value is expressed in its value. If his capacity for labor remains unsold, the laborer derives no benefit from it, but rather he will feel it to be a cruel nature-imposed necessity that this capacity has cost for its production a definite amount of the means of subsistence and that it will continue to do so for its reproduction. He will then agree with Sismondi: “that capacity for labor … is nothing unless it is sold.”11
One consequence of the peculiar nature of labor-power as a commodity is, that its use-value does not, on the conclusion of the contract between the buyer and seller, immediately pass into the hands of the former. Its value, like that of every other commodity, is already fixed before it goes into circulation, since a definite quantity of social labor has been spent upon it; but its use-value consists in the subsequent exercise of its force. The alienation of labor-power and its actual appropriation by the buyer, its employment as a use-value, are separated by an interval of time. But in those cases in which the formal alienation by sale of the use-value of a commodity, is not simultaneous with its actual delivery to the buyer, the money of the latter usually functions as means of payment.12 In every country in which the capitalist mode of production reigns, it is the custom not to pay for labor-power before it has been exercised for the period fixed by the contract, as for example, the end of each week. In all cases, therefore, the use-value of the labor-power is advanced to the capitalist: the laborer allows the buyer to consume it before he receives payment of the price; he everywhere gives credit to the capitalist. That this credit is no mere fiction, is shown not only by the occasional loss of wages on the bankruptcy of the capitalist,13 but also by a series of more enduring consequences.14 Nevertheless, whether money serves as a means of purchase or as a means of payment, this makes no alteration in the nature of the exchange of commodities. The price of the labor-power is fixed by the contract, although it is not realized till later, like the rent of a house. The labor-power is sold, although it is only paid for at a later period. It will, therefore, be useful, for a clear comprehension of the relation of the parties, to assume provisionally, that the possessor of labor-power, on the occasion of each sale, immediately receives the price stipulated to be paid for it.
We now know how the value paid by the purchaser to the possessor of this peculiar commodity, labour-power, is determined. The use-value which the former gets in exchange, manifests itself only in the actual utilisation, in the consumption of the labour-power. The money-owner buys everything necessary for this purpose, such as raw material, in the market, and pays for it at its full value. The consumption of labour-power is at one and the same time the production of commodities and of surplus-value. The consumption of labour-power is completed, as in the case of every other commodity, outside the limits of the market or of the sphere of circulation. Accompanied by Mr. Moneybags and by the possessor of labour-power, we therefore take leave for a time of this noisy sphere, where everything takes place on the surface and in view of all men, and follow them both into the hidden abode of production, on whose threshold there stares us in the face “No admittance except on business.” Here we shall see, not only how capital produces, but how capital is produced. We shall at last force the secret of profit making.
This sphere that we are deserting, within whose boundaries the sale and purchase of labor-power goes on, is in fact a very Eden of the innate rights of man. There alone rule Freedom, Equality, Property and Bentham. Freedom, because both buyer and seller of a commodity, say of labor-power, are constrained only by their own free will. They contract as free agents, and the agreement they come to, is but the form in which they give legal expression to their common will. Equality, because each enters into relation with the other, as with a simple owner of commodities, and they exchange equivalent for equivalent. Property, because each disposes only of what is his own. And Bentham, because each looks only to himself. The only force that brings them together and puts them in relation with each other, is the selfishness, the gain and the private interests of each. Each looks to himself only, and no one troubles himself about the rest, and just because they do so, do they all, in accordance with the pre-established harmony of things, or under the auspices of an all-shrewd providence, work together to their mutual advantage, for the common weal and in the interest of all.
On leaving this sphere of simple circulation or of exchange of commodities, which furnishes the “Free-trader Vulgaris” with his views and ideas, and with the standard by which he judges a society based on capital and wages, we think we can perceive a change in the physiognomy of our dramatis personae. He, who before was the money-owner, now strides in front as capitalist; the possessor of labor-power follows as his laborer. The one with an air of importance, smirking, intent on business; the other, timid and holding back, like one who is bringing his own hide to market and has nothing to expect but – a hiding.
Notes
1 “In the form of money … capital is productive of no profit.” (Ricardo: “Princ. of Pol. Econ.,” p. 267.)
2 In encyclopedias of classical antiquities we find such nonsense as this — that in the ancient world capital was fully developed, “except that the free laborer and a system of credit was wanting.” Mommsen also, in his “History of Rome,” commits, in this respect, one blunder after another.
3 Hence legislation in various countries fixes a maximum for labor-contracts. Wherever free labor is the rule, the laws regulate the mode of terminating this contract. In some States, particularly in Mexico (before the American Civil War, also in the territories taken from Mexico, and also, as a matter of fact, in the Danubian provinces till the revolution effected by Kusa), slavery is hidden under the form of peonage. By means of advances, repayable in labor, which are handed down from generation to generation, not only the individual laborer, but his family, become, de facto, the property of other persons and their families. Juarez abolished peonage. The so-called Emperor Maximilian re-established it by a decree, which, in the House of Representatives at Washington, was aptly denounced as a decree for the re-introduction of slavery into Mexico. “I may make over to another the use, for a limited time, of my particular bodily and mental aptitudes and capabilities; because in consequence of this restriction, they are impressed with a character of alienation with regard to me as a whole. But by the alienation of all my labor-time and the whole of my work, I should be converting the substance itself, in other words, my general activity and reality, my person, into the property of another.” (Hegel, “Philosophie des Rechts.” Berlin, 1840, p. 104, § 67.)
4 The capitalist epoch is therefore characterized by this, that labor-power takes in the eyes of the laborer himself the form of a commodity which is his property; his labor consequently becomes wage-labor. On the other hand, it is only from this moment that the produce of labor universally becomes a commodity.
5 “The value or worth of a man, is as of all other things his price — that is to say, so much as would be given for the use of his power.” (Th. Hobbes: “Leviathan” in Works, Ed. Molesworth. Lond. 1839-44, v. iii. p. 76.)
6 Hence the Roman Villicus, as overlooker of the agricultural slaves, received “more meagre fare than working slaves, because his work was lighter.” (Th. Mommsen, Röm. Geschichte, 1856, p. 810.)
7 Compare W. Th. Thornton: “Over-population and its Remedy,” Lond., 1846.
8 Petty.
9 “Its (labour’s) natural price … consists in such a quantity of necessaries and comforts of life, as, from the nature of the climate, and the habits of the country, are necessary to support the laborer, and to enable him to rear such a family as may preserve, in the market, an undiminished supply of labor.” (R. Torrens: “An Essay on the External Corn Trade.” Lond. 1815, p. 62.) The word labor is here wrongly used for labor-power.
10 Rossi: “Cours d’Econ. Polit.,” Bruxelles, 1842, p. 370.
11 Sismondi: “Nouv. Princ. etc.,” t. I, p. 112.
12 “All labor is paid after it has ceased.” (“An Inquiry into those Principles Respecting the Nature of Demand,” &c., p. 104.) Le crédit commercial a dû commencer au moment où l’ouvrier, premier artisan de la production, a pu, au moyen de ses économies, attendre le salaire de son travail jusqu’à la fin de la semaine, de la quinzaine, du mois, du trimestre, &c.” [“The system of commercial credit had to start at the moment when the labourer, the prime creator of products, could, thanks to his savings, wait for his wages until the end of the week.”] (Ch. Ganilh: “Des Systèmes d’Econ. Polit.” 2éme édit. Paris, 1821, t. II, p. 150.)
13 “L’ouvrier prête son industrie,” but adds Storch slyly: he “risks nothing” except “de perdre son salaire … l’ouvrier ne transmet rien de matériel.” [“The labourer lends his industry … the loss of his wages … the labourer does not hand over anything of a material nature.”] (Storch: “Cours d’Econ. Polit.” Pétersbourg, 1815, t. II., p. 37.)
14 One example. In London there are two sorts of bakers, the “full priced,” who sell bread at its full value, and the “undersellers,” who sell it under its value. The latter class comprises more than three-fourths of the total number of bakers. (p. xxxii in the Report of H. S. Tremenheere, commissioner to examine into “the grievances complained of by the journeymen bakers,” &c., Lond. 1862.) The undersellers, almost without exception, sell bread adulterated with alum, soap, pearl ashes, chalk, Derbyshire stone-dust, and such like agreeable nourishing and wholesome ingredients. (See the above cited Blue book, as also the report of “the committee of 1855 on the adulteration of bread,” and Dr. Hassall’s “Adulterations Detected,” 2nd Ed. Lond. 1861.) Sir John Gordon stated before the committee of 1855, that “in consequence of these adulterations, the poor man, who lives on two pounds of bread a day, does not now get one fourth part of nourishing matter, let alone the deleterious effects on his health.” Tremenheere states (l.c., p. xlviii), as the reason, why a very large part of the working-class, although well aware of this adulteration, nevertheless accept the alum, stone-dust, &c., as part of their purchase: that it is for them “a matter of necessity to take from their baker or from the chandler’s shop, such bread as they choose to supply.” As they are not paid their wages before the end of the week, they in their turn are unable “to pay for the bread consumed by their families, during the week, before the end of the week,” and Tremenheere adds on the evidence of witnesses, “it is notorious that bread composed of those mixtures, is made expressly for sale in this manner.” In many English and still more Scotch agricultural districts, wages are paid fortnightly and even monthly; with such long intervals between the payments, the agricultural laborer is obliged to buy on credit…. He must pay higher prices, and is in fact tied to the shop which gives him credit. Thus, at Horningham in Wilts, for example, where the wages are monthly, the same flour that he could buy elsewhere at 1s 10d per stone, costs him 2s 4d per stone. (“Sixth Report” on “Public Health” by “The Medical Officer of the Privy Council, &c., 1864,” p.264.) “The block printers of Paisley and Kilmarnock enforced, by a strike, fortnightly, instead of monthly payment of wages.” (“Reports of the Inspectors of Factories for 31st Oct., 1853,” p. 34.) As a further pretty result of the credit given by the workmen to the capitalist, we may refer to the method current in many English coal mines, where the laborer is not paid till the end of the month, and in the meantime, receives sums on account from the capitalist, often in goods for which the miner is obliged to pay more than the market price (Truck-system). “It is a common practice with the coal masters to pay once a month, and advance cash to their workmen at the end of each intermediate week. The cash is given in the shop” (i.e., the Tommy shop which belongs to the master); “the men take it on one side and lay it out on the other.” (“Children’s Employment Commission, III. Report,” Lond. 1864, p. 38, n. 192.)
Chapter 7 – The Labor-Process and the Process of Producing Surplus-Value
Chapter 5 – Contradictions in the General Formula of Capital
Questions
What is the only commodity whose use-value creates value, according to Marx?
→ Labor-power, because its consumption (work) produces new value and surplus-value.
What conditions must exist for labor-power to be sold as a commodity?
→ The worker must be legally free and economically compelled to sell their labor-power.
Why can’t value originate from money itself or resale of commodities?
→ Because money is static value and resale just returns the form of value, not creates it.
How is the value of labor-power determined?
→ By the socially necessary labor-time required to produce the worker’s means of subsistence.
Why does Marx call labor-power a ‘peculiar commodity’?
→ Because its value is realized only after its sale, through the act of labor, not upon purchase.
What historical process allows labor-power to appear as a commodity?
→ The separation of workers from the means of production and subsistence, through past revolutions.
Why does Marx say the laborer must sell labor for a limited period?
→ To avoid becoming a slave and retain legal ownership over their labor-power.
How does wage labor create surplus-value for the capitalist?
→ The worker produces more value during work than the value of their wages.
Why does Marx criticize the idea of ‘free exchange’ in the labor market?
→ Because while it appears equal and free, it masks underlying exploitation and coercion.
What transformation occurs when the labor contract is executed?
→ The money-owner becomes a capitalist; the laborer becomes a worker—signifying exploitation begins.


Pingback: Chapter 5 – Contradictions in the General Formula of Capital
Pingback: Chapter 7 – The Labor-Process and the Process of Producing Surplus-Value